In TMSi — an Artinis company blog, you will find the latest trends in EEG and HD-EMG, related studies and applications, insights from the leaders of EEG/HD-EMG, not to mention detailed tips and tricks for your research!

Types of EEG Electrodes: Gel, Water, and Dry
Explaining the differences, advantages, and disadvantages of various EEG electrode types: Gel, Water, and Dry.

Event-Related Potentials in EEG
ERP is the neural response associated with a specific sensory, cognitive, or motor event (e.g. a stimulus). An ERP is often recorded using scalp electroencephalography (EEG) and looks at the average change in voltage over time starting at the onset of the stimulus over multiple trials. ERP measurements have a precise temporal resolution, which is useful in testing perception and attention.1 This information can be used to evaluate brain functioning by looking at how the brain normally processes information, as well as viewing how this processing may differ in neurological or psychiatric disorders.
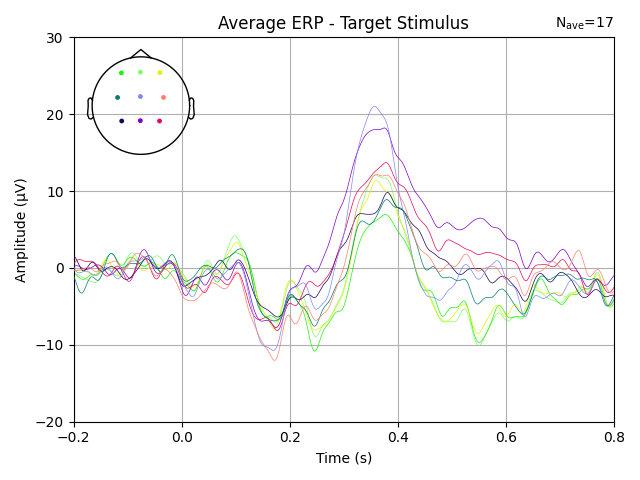
What is the P300 in Event-Related Potentials (ERPs)?
This blog describes what the P300 is and how you can detect it. It includes a practical example of how a P300 response was measured using TMSi's SAGA, including the experimental protocol, a sample dataset, and all acquisition and processing codes. At the end of this blog, you will be able to download this sample data set and run through the scripts to view the P300 yourself.

Motion Artifacts on EEG
A common problem in measurement setups where the subject is allowed to move around is the movement artifact. Movement artifacts on EEG measurements originate from two different phenomena: the movement of the cables and the movement of the electrode.

Basics of Measuring Bioelectricity in humans
Bio-electricity refers to the measurable potential differences between two points on the body, providing valuable insights into the body's electrical activity. Understanding the origins of these potentials and the challenges involved in measuring them is essential for accurate interpretation and application.
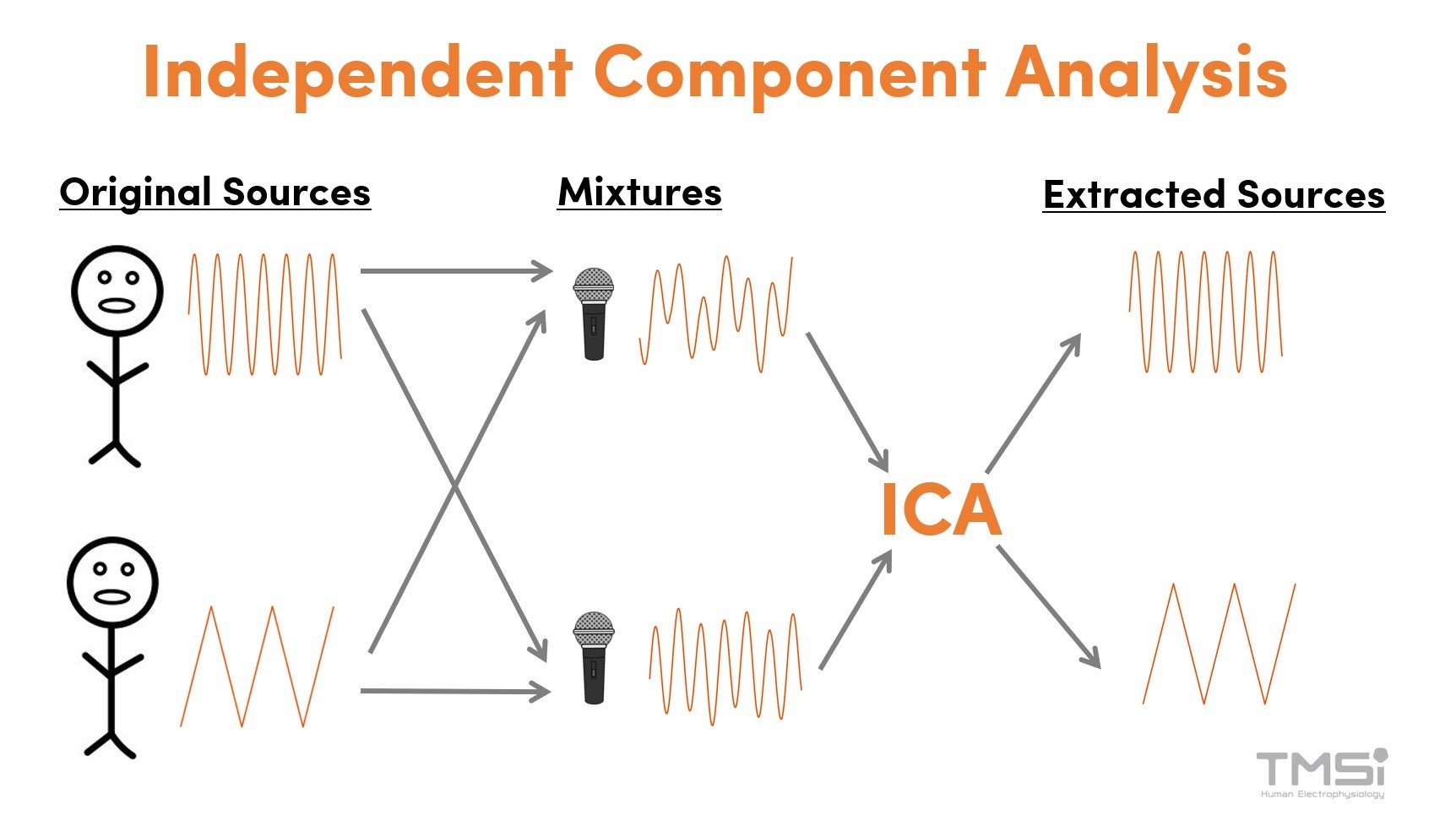
Removing Artifacts From EEG Data Using Independent Component Analysis (ICA)
Eye movements and blinks cause significant EEG artifacts, with blink artifacts being much larger in amplitude than EEG signals. Preventing eye movement artifacts is challenging, as restricting blinking or gaze can increase cognitive load. Post-processing methods like Independent Component Analysis (ICA) effectively remove these artifacts while preserving the data.

Common non-physiological (external) EEG artifacts
Learn how to recognize non-physiological (external) artifacts in the electroencephalogram (EEG) and how to prevent them.

Common physiological EEG artifacts
A guide on how to recognize physiological artifacts in the electroencephalogram (EEG) and how to manage them.

What is Neurofeedback?
Neurofeedback is a method that uses real-time brain activity to provide individuals with feedback on their brain function. Brain activity is often measured with electroencephalography (EEG). The goal of neurofeedback is to help individuals gain more control over their brain function. In this process, the user is provided with positive feedback for desirable brain activity and negative feedback for undesirable brain activity. This feedback mechanism is hypothesized to enable users to train and regulate their brain activity over time.
