In TMSi — an Artinis company blog, you will find the latest trends in EEG and HD-EMG, related studies and applications, insights from the leaders of EEG/HD-EMG, not to mention detailed tips and tricks for your research!

Mains Interference
Electrophysiological measurements often include interference from mains electricity, typically 220 V/50 Hz in Europe and 110 V/60 Hz in other regions. Even when using battery-powered amplifiers, mains interference can still affect recordings due to various pathways. Understanding these interference mechanisms is key to minimizing their impact.

Basics of Measuring Bioelectricity in humans
Bio-electricity refers to the measurable potential differences between two points on the body, providing valuable insights into the body's electrical activity. Understanding the origins of these potentials and the challenges involved in measuring them is essential for accurate interpretation and application.
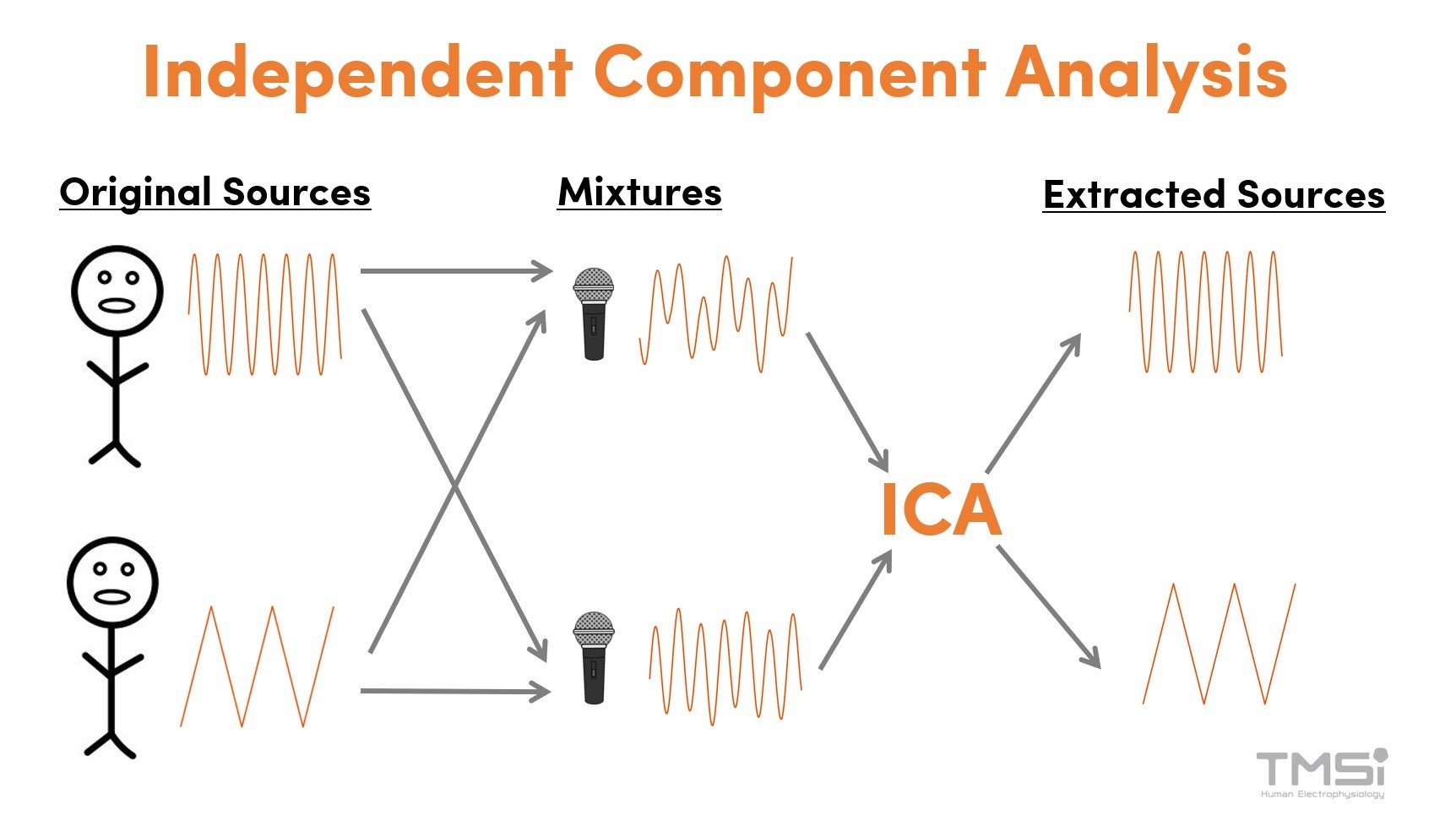
Removing Artifacts From EEG Data Using Independent Component Analysis (ICA)
Eye movements and blinks cause significant EEG artifacts, with blink artifacts being much larger in amplitude than EEG signals. Preventing eye movement artifacts is challenging, as restricting blinking or gaze can increase cognitive load. Post-processing methods like Independent Component Analysis (ICA) effectively remove these artifacts while preserving the data.

Common non-physiological (external) EEG artifacts
Learn how to recognize non-physiological (external) artifacts in the electroencephalogram (EEG) and how to prevent them.

Common physiological EEG artifacts
A guide on how to recognize physiological artifacts in the electroencephalogram (EEG) and how to manage them.

What is Neurofeedback?
Neurofeedback is a method that uses real-time brain activity to provide individuals with feedback on their brain function. Brain activity is often measured with electroencephalography (EEG). The goal of neurofeedback is to help individuals gain more control over their brain function. In this process, the user is provided with positive feedback for desirable brain activity and negative feedback for undesirable brain activity. This feedback mechanism is hypothesized to enable users to train and regulate their brain activity over time.

What Is Electromyography (EMG)?
This blog post contains everything you need to know about muscle structure, signal characteristics, types of EMG, and applications.

Announcing Artinis’ Acquisition of TMSi: A Strategic Partnership
We are proud to announce that Artinis has acquired TMSi. This acquisition allows both companies to leverage over two decades of combined expertise and technology, enabling us to offer even more advanced solutions for the medical and scientific markets.
