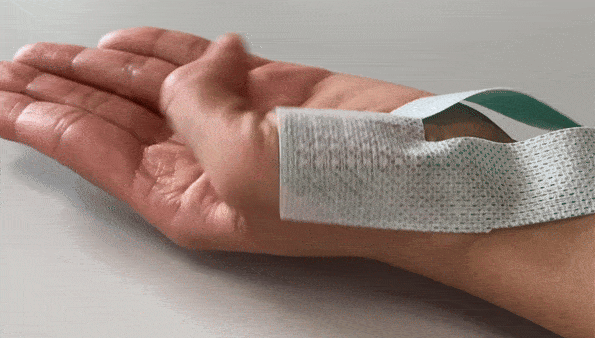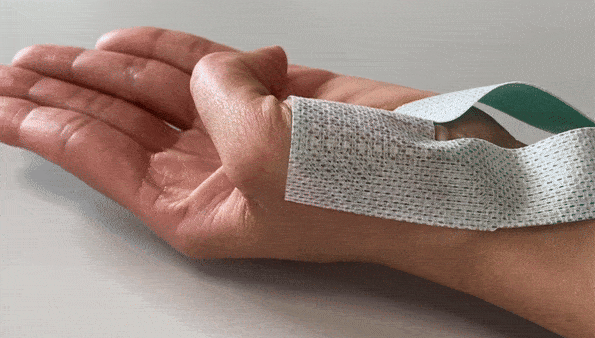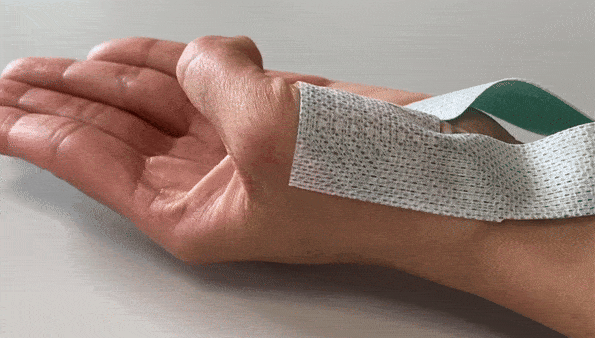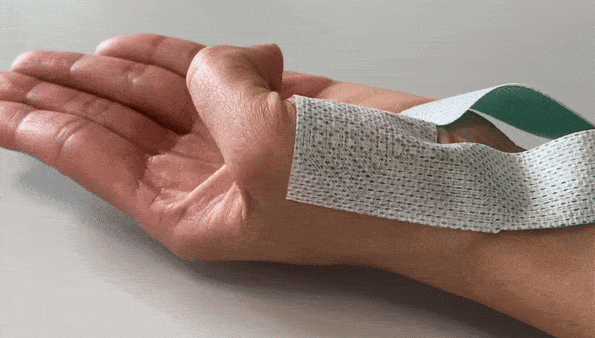
HD-EMG Accessories
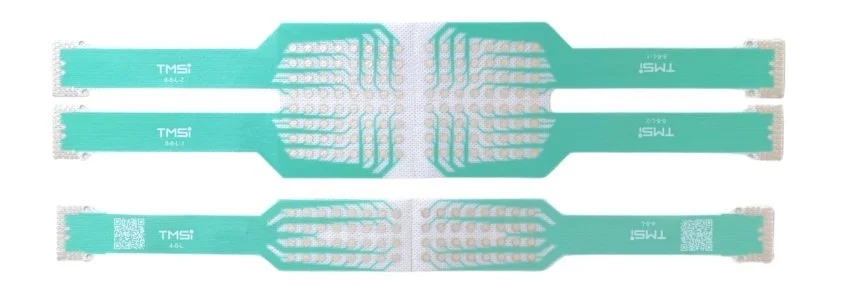
Textile HD-EMG Grids
High-density EMG (HD-EMG) grids are used to measure muscle activation non-invasively and with high resolution, providing insights into the neuromuscular system. It is important to measure this detailed information as accurately as possible, that is why we have developed these Textile HD-EMG Grids.
Why Our Textile Grids
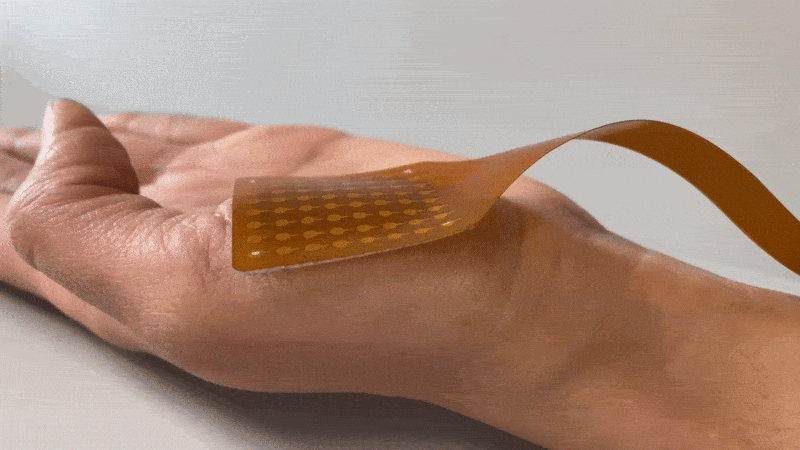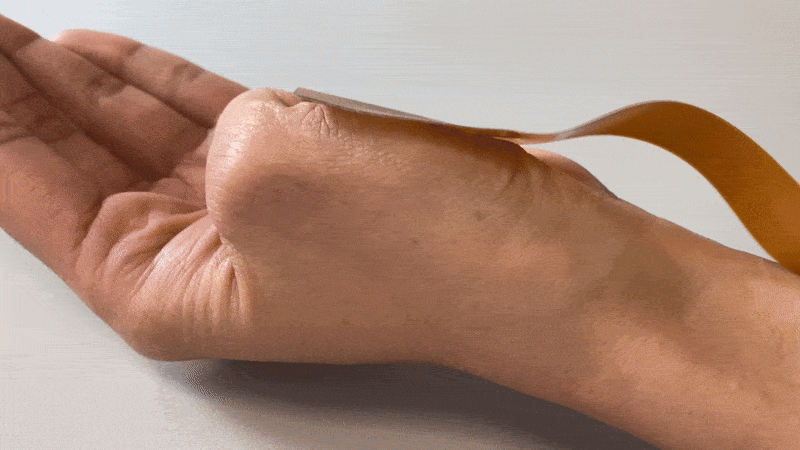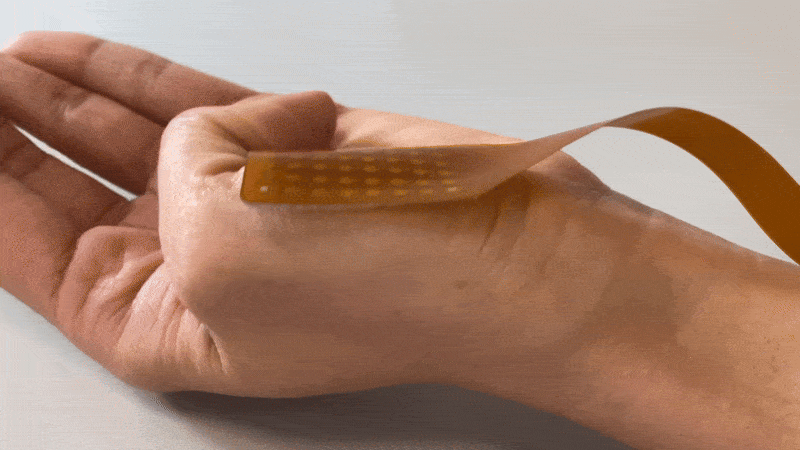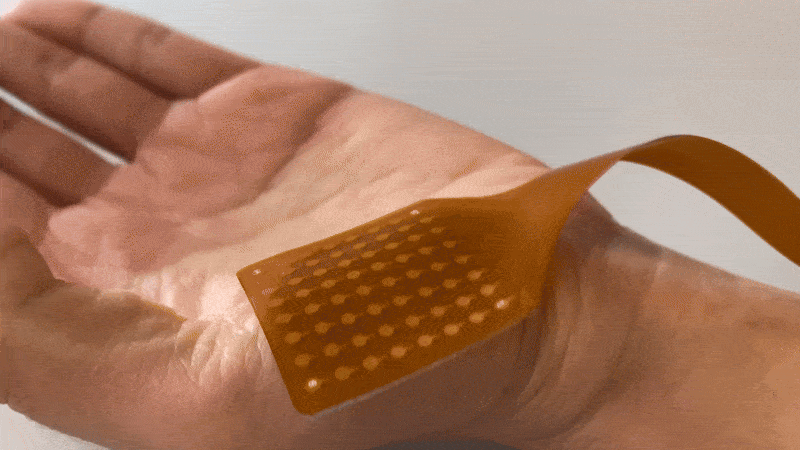
Textile HD-EMG Grids are very suitable for use on contracting muscles, as they are flexible yet durable.
-
The Textile HD-EMG Grids come with Ag/AgCl electrodes, so that the signal quality remains stable over the course of the recording.
-
We have various grid configurations in 32 or 64-channel grids. Additionally, it is possible to place two grids side by side for an extended configuration of 128-channels. Our 8×8 L and S grids can also be cut into two 4×8 L and S grids for further customization.
-
The Textile HD-EMG Grids can be reused. More information about reusing the grids can be found here. Additional double-sided adhesives for reusing the grids are available for the 8×8 (large and small) and the 4×8-large layout.
-
The Textile HD-EMG Grid Adapter Cable is a robust, lightweight, actively shielded cable. The cable comes in a 32-channel or 64-channel version.
-
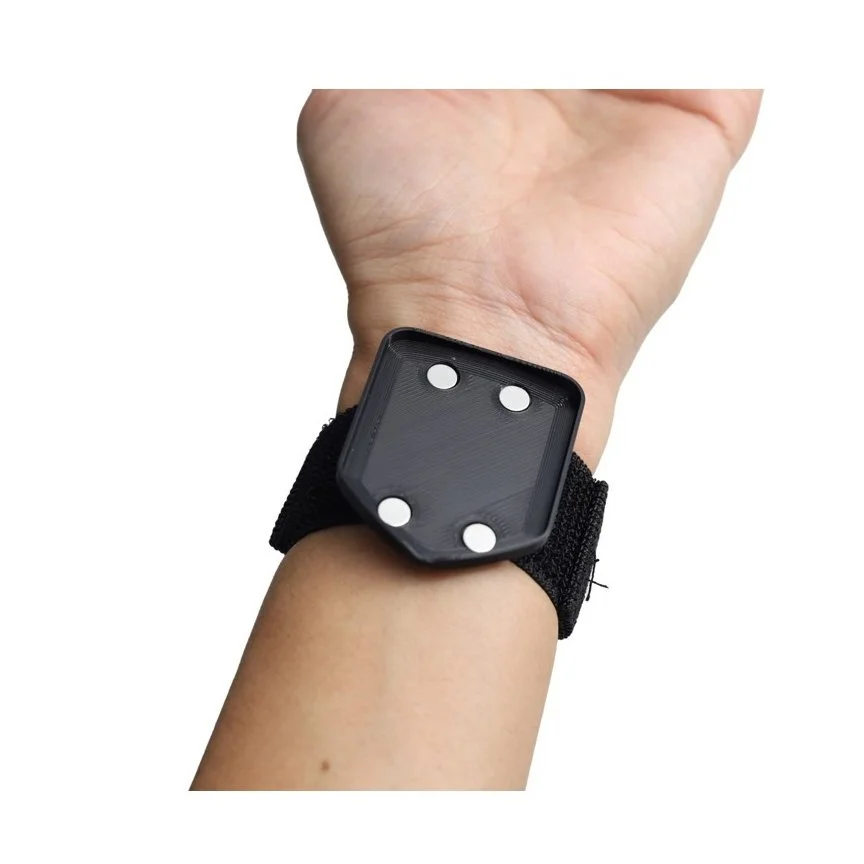
Secure the cable anywhere on the body using the unique Textile HD-EMG Grid Cradle. The cradle can be attached to 4 different sizes of straps to fit around different limb sizes. This easy-to-use cradle holds the adapter cable in place during all movements.
Selections to Match Your Research Needs
Extended Configurations
Place two Textile HD-EMG Grids side by side for an extended configuration. For example, create a 4×16 grid by cutting an 8×8 grid in half and placing them head-to-head. For 128 channels, place txwo 8×8 grids head-to-head to form an 8×16 grid.
Cable and Straps
Customization Options
The 8×8 L and S grids can be cut into two 4×8 L and S grids.
If you would like an alternative configuration for your research, it is possible to design a custom grid. Please contact us at askforinfo@artinis.com for more information.
Textile HD-EMG Grid Adapter Cable
The Textile HD-EMG Grid Adapter Cable is a robust, lightweight, actively shielded cable. The cable comes in a 32-channel or 64-channel version.
Secure Fit
Secure the cable anywhere on the body using the unique Textile HD-EMG Grid Cradle. The cradle can be attached to 4 different sizes of straps to fit around different limb sizes. This easy-to-use cradle holds the adapter cable in place during all movements.
Various Configurations
Our grids are available in 32- or 64-channel variants and two inter-electrode distance (IED) options: small (4 mm) or large (8.75 mm). The IED measurement refers to the spacing between adjacent electrodes (center to center) in a grid.
32 channels, 4×8 layout, Small (4mm IED)*
32 channels, 4×8 layout, Large (8.75mm IED)
64 channels, 6×11 layout, Small (4mm IED)
64 channels, 6×11 layout, Large (8.75mm IED)
64 channels, 8×8 layout, Small (4mm IED)
64 channels, 8×8 layout, Large (8.75mm IED)
*Future product, not yet available.
HD-EMG Applications
Examples of what you can do with our Textile HD-EMG Grids:
Muscle Fiber Properties
Investigate the characteristics and behavior of muscle fibers to gain insights into muscle physiology.
Spatial Muscle Mapping
Conduct detailed spatial mapping of muscle activity for comprehensive analysis of muscle behavior, synergy, and function.Motor Unit Decomposition
Record and evaluate individual motor units to explore neuromuscular function.
Behind the Textile HD-EMG Grids
Due to the flexibility of the used fabric, the electrodes form to the skin perfectly, reducing the probability of movement artifacts due to the rigid material of current HD-EMG grids on the market. So whether monitoring a single muscle during isometric exercises or studying multiple muscle groups in dynamic movements like walking or jumping, the grid’s flexible fabric improves signal quality and reduces the need for artifact removal.
From Problem…
The previous generation HD-EMG grids are made of PCB material, which is hard to place on double-curved and dynamic locations. Researchers typically experience electrodes detaching when the grid is partially lifted from the skin. This results in artifacts in the signal, analyzing HD-EMG signals more challenging and time-consuming.
…to our Solution!
TMSi developed a revolutionary Textile HD-EMG Grid to solve these typical problems. The Textile HD-EMG Grids are made of slightly stretchable, textile material with great adhesion. Because of these properties, the grid prevents movement artifacts and stays perfectly on the skin -even when placed on challenging surfaces.
Scroll down & prove the data quality recorded with the Textile HD-EMG grids!
Check the Data for Yourself
The Textile HD-EMG grids deliver high-quality HD-EMG signals with exceptional precision. To showcase their performance, we provide three example recordings, enabling you to verify the outstanding data quality for yourself.
What was recorded?
The HD-EMG measurement has been done using the 8-8-L Textile Grid (8x8 topology, 8.75 mm IED) on the gastrocnemius muscle, see Figure 1. The 64-channel grid covers both the medial and lateral head to show the flexibility of the grid. The grid can also be cut in half, in two 32-channel variants to cover each head more precisely.
What does the data show?
Below, two types of analysis of the data are shown. Figure 1 shows the average power frequency spectrum of the raw signal of all 64 channels for the three measurements. In the recordings where muscle activity was recorded (constant calf raise and squat jumps), no mains interference can be seen. For the "rest” condition, as there is no muscle activity present and therefore lower power in general, there are small peaks at 50 Hz.
Figure 2 shows four seconds of squat jump data from a single row of channels. Pre-processing only included the removal of the offset with no further filtering. In the plot, you can see that the signal remains stable when jumping and when landing.
Figure 1: Average frequency spectrum of the sample data during rest, constant calf raise, and squat jumps.
Figure 2: Single row of raw HD-EMG data showing two squat jumps.
How can I view or analyze the data myself?
You can import the recordings into our file viewer to view the data. To perform data analysis, you can use TMSi Python interface to import the recordings into Python. Please follow the installation instructions in the Documentation TMSi Python Interface. After installation, you can load the data into Python with the example script example_file_reader.py in the folder examples_reading_data of the TMSi Python Interface.
Motor Unit Decomposition (MUD)
It is possible to do Motor Unit Decomposition with our Textile HD-EMG Grids
Motor Unit Decomposition is a technique used to separate and analyze individual motor unit (MU) activity from the combined electrical signals recorded by EMG. HD-EMG provides high spatial resolution, allowing for precise detection and decomposition of motor units from complex muscle activity.
Watch A Deep Dive into Motor Unit Decomposition
Credit: I-SpinSAGA is an adaptation from I-Spin live which has been developed by J. Rossato et al. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.88670.1
Take a closer look at the grids in this Signal Demonstration Video
Products and Accessories
Artinis EEG/HD-EMG products are intended for research purposes only and are not designed, marketed, or authorized for use in the diagnosis, prevention, or treatment of any disease or medical condition.